参考 http://const.me/articles/simd/simd.pdf
https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/docs/intrinsics-guide/index.html#cats=Arithmetic&expand=3904,3913,4011,34,4014,4602,4011&techs=MMX,AVX_512,AMX,SVML,Other&ig_expand=11
示例:对4个数字求平方
void mul4_scalar( float* ptr )
{
for( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
const float f = ptr[ i ];
ptr[ i ] = f * f;
}
}
使用SIMD
void mul4_vectorized( float* ptr )
{
__m128 f = _mm_loadu_ps( ptr );
f = _mm_mul_ps( f, f );
_mm_storeu_ps( ptr, f );
}
解释:
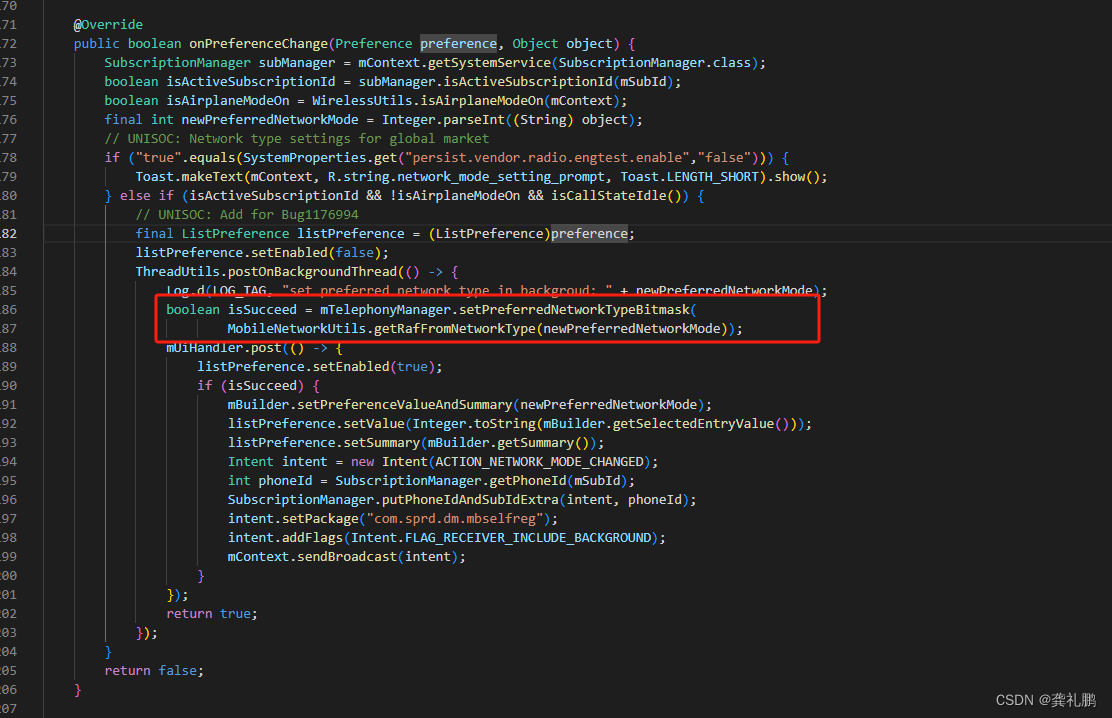
函数 _mm_loadu_ps
Load 128-bits (composed of 4 packed single-precision (32-bit) floating-point elements) from memory into dst. mem_addr does not need to be aligned on any particular boundary.
加载128比特数据(4个float类型)
函数__m128 _mm_mul_ps (__m128 a, __m128 b)
Synopsis
__m128 _mm_mul_ps (__m128 a, __m128 b)
#include <xmmintrin.h>
Instruction: mulps xmm, xmm
CPUID Flags: SSE
Description
Multiply packed single-precision (32-bit) floating-point elements in a and b, and store the results in dst.
函数 void _mm_storeu_ps (float* mem_addr, __m128 a)
#include <immintrin.h>
Instruction: movups m128, xmm
CPUID Flags: SSE
Description
Store 128-bits (composed of 4 packed single-precision (32-bit) floating-point elements) from a into memory. mem_addr does not need to be aligned on any particular boundary.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <immintrin.h>
void vectorAddSSE(const std::vector<double>& v1, const std::vector<double>& v2, std::vector<double>& result)
{
// Ensure vectors are of the same size
size_t size = v1.size();
if (size != v2.size() || size != result.size())
{
std::cerr << "Vector sizes mismatch." << std::endl;
return;
}
// Process 4 elements at a time using SSE
for (size_t i = 0; i < size; i += 4)
{
// Load 4 double values from each vector
__m256d vec1 = _mm256_loadu_pd(&v1[i]);
__m256d vec2 = _mm256_loadu_pd(&v2[i]);
// Perform vector addition
__m256d resultVec = _mm256_add_pd(vec1, vec2);
// Store the result back to the result vector
_mm256_storeu_pd(&result[i], resultVec);
}
// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSE
for (size_t i = size - size % 4; i < size; ++i)
{
result[i] = v1[i] + v2[i];
}
}
int main()
{
std::vector<double> v1 = {1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0};
std::vector<double> v2 = {5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0};
std::vector<double> result(4);
vectorAddSSE(v1, v2, result);
// Output the result
std::cout << "Result: ";
for (double value : result)
{
std::cout << value << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
进阶:求矩阵的和
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<string>
template <typename T>
class Matrix {
private:
std::vector<std::vector<T>> matrix;
int m_nRows;
int m_nCols;
public:
// 构造函数
Matrix(int m_nRows, int m_nCols, const T& initial = T());
// 获取矩阵的行数和列数
int numRows() const;
int numCols() const;
// 获取矩阵中特定位置的元素
T& at(int row, int col);
// 获取矩阵元素的值
T get(int row, int col) const;
// 更新矩阵元素的值
void set(int row, int col, const T& value);
// 矩阵加法
Matrix<T> operator+(const Matrix<T>& other) const;
// 矩阵减法
Matrix<T> operator-(const Matrix<T>& other) const;
// 矩阵乘法
Matrix<T> operator*(const Matrix<T>& other) const;
//[]操作符重载
const std::vector<T>& operator[](size_t row) const;
//[]操作符重载
std::vector<T>& operator[](size_t row);
// 掩膜操作
Matrix<T> mask(const Matrix<T>& mask, T value = static_cast<T>(0));
// 统计矩阵中某个值的数量
int countValue(const T& value) const;
//保存到图片
void saveImage(const std::string& filename);
void printPart(int x, int y, int step, std::string s = "");
private:
};
//sse逐点相
// lineAdd_sse 的特化的前向声明
template <typename T>
inline void lineAdd_sse(const T* left, const T* right, int nCounts, T* save) {};
template <>
inline void lineAdd_sse(const double* left, const double* right, int size, double* save);
template <>
inline void lineAdd_sse(const float* left, const float* right, int size, float* save);
template <>
inline void lineAdd_sse(const int* left, const int* right, int size, int* save);
/ 矩阵加法 sse
template <typename T>
Matrix<T> MatrixAdditionSSE(const Matrix<T>& m1, const Matrix<T>& m2);
实现
template<>
inline void lineAdd_sse(const float* left, const float* right, int size, float* save)
{
//Process 8 float elements at a time using SSE
for (int i = 0; i < size-7; i += 8)
{
_mm256_storeu_ps(save + i, _mm256_add_ps(_mm256_loadu_ps(left + i), _mm256_loadu_ps(right + i)));
}
// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSE
for (size_t i = size - size % 8; i < size; ++i)
{
save[i] = left[i] + right[i];
}
}
template<>
inline void lineAdd_sse(const double* left, const double* right, int size, double* save)
{
// Process 4 double elements at a time using SSE
for (size_t i = 0; i < size-3; i += 4)
{
// Load 4 double values from each vector
__m256d vec1 = _mm256_loadu_pd(&left[i]);
__m256d vec2 = _mm256_loadu_pd(&right[i]);
// Perform vector addition
__m256d resultVec = _mm256_add_pd(vec1, vec2);
// Store the result back to the result vector
_mm256_storeu_pd(&save[i], resultVec);
}
// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSE
for (size_t i = size - size % 4; i < size; ++i)
{
save[i] = left[i] + right[i];
}
}
template <>
inline void lineAdd_sse(const int* left, const int* right, int size, int* save)
{
// Process 8 int elements at a time using SSE
for (int i = 0; i < size - 7; i += 8)
{
__m256i vec1 = _mm256_loadu_si256(reinterpret_cast<const __m256i*>(&left[i]));
__m256i vec2 = _mm256_loadu_si256(reinterpret_cast<const __m256i*>(&right[i]));
// Perform vector addition
__m256i resultVec = _mm256_add_epi32(vec1, vec2);
// Store the result back to the result vector
_mm256_storeu_si256(reinterpret_cast<__m256i*>(&save[i]), resultVec);
}
// Process the remaining elements (if any) without SSE
for (int i = size - size % 8; i < size; ++i)
{
save[i] = left[i] + right[i];
}
}
template <typename T>
Matrix<T> MatrixAdditionSSE(const Matrix<T>& m1, const Matrix<T>& m2)
{
static_assert(sizeof(T) == sizeof(float) || sizeof(T) == sizeof(double) || sizeof(T) == sizeof(int),
"Unsupported element type for SSE");
if (m1.numRows() != m2.numRows() || m1.numCols() != m2.numCols())
{
throw std::invalid_argument("Matrix dimensions don't match for addition");
}
Matrix<T> result(m1.numRows(), m1.numCols());
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
const int numThreads = std::thread::hardware_concurrency(); // Number of available threads
const int rowsPerThread = (m1.numRows() + numThreads - 1) / numThreads; // Rows per thread
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; ++i)
{
threads.emplace_back([&m1, &m2, &result, i, rowsPerThread]()
{
for (int row = i * rowsPerThread; row < std::min((i + 1) * rowsPerThread, result.numRows()); ++row)
{
lineAdd_sse(&m1[row][0], &m2[row][0], result.numCols(), &result[row][0]);
}
});
}
for (auto& thread : threads)
{
thread.join();
}
return std::move(result);
}